Rosalind Franklin Personality Type
British chemist, biophysicist and X-ray crystallographer (1920–1958)
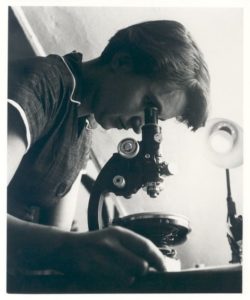
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 1920 – 16 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal, and graphite. Although her works on coal and viruses were appreciated in her lifetime, her contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA were largely unrecognized during her life, for which she has been variously referred to as the "wronged heroine", the "dark lady of DNA", the "forgotten heroine", a "feminist icon", and the "Sylvia Plath of molecular biology".She graduated in 1941 with a degree in natural sciences from Newnham College, Cambridge, and then enrolled for a PhD in physical chemistry under Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, the 1920 Chair of Physical Chemistry at the University of Cambridge. Disappointed by Norrish's lack of enthusiasm, she took up a research position under the British Coal Utilisation Research Association (BCURA) in 1942. The research on coal helped her earn a PhD from Cambridge in 1945. Moving to Paris in 1947 as a chercheur (postdoctoral researcher) under Jacques Mering at the Laboratoire Central des Services Chimiques de l'État, she became an accomplished X-ray crystallographer. After joining King's College London in 1951 as a research associate, she discovered the key properties of DNA, which eventually facilitated the correct description of the double helix structure of DNA. Owing to disagreement with her director, John Randall, and her colleague Maurice Wilkins, she was compelled to move to Birkbeck College in 1953.